Maximizing Performance & Boosting Efficiency
Benefiting Factors of Micro-Aid®
Optimizes Nutrient Utilization
Micro-Aid® promotes a healthier gut environment via a reduction in intestinal ammonia, mucosa tissue turn-over rate & maintenance energy demands.
Aids in establishing ideal gastrointestinal tract health allowing for optimum nutrient utilization & peak animal performance.
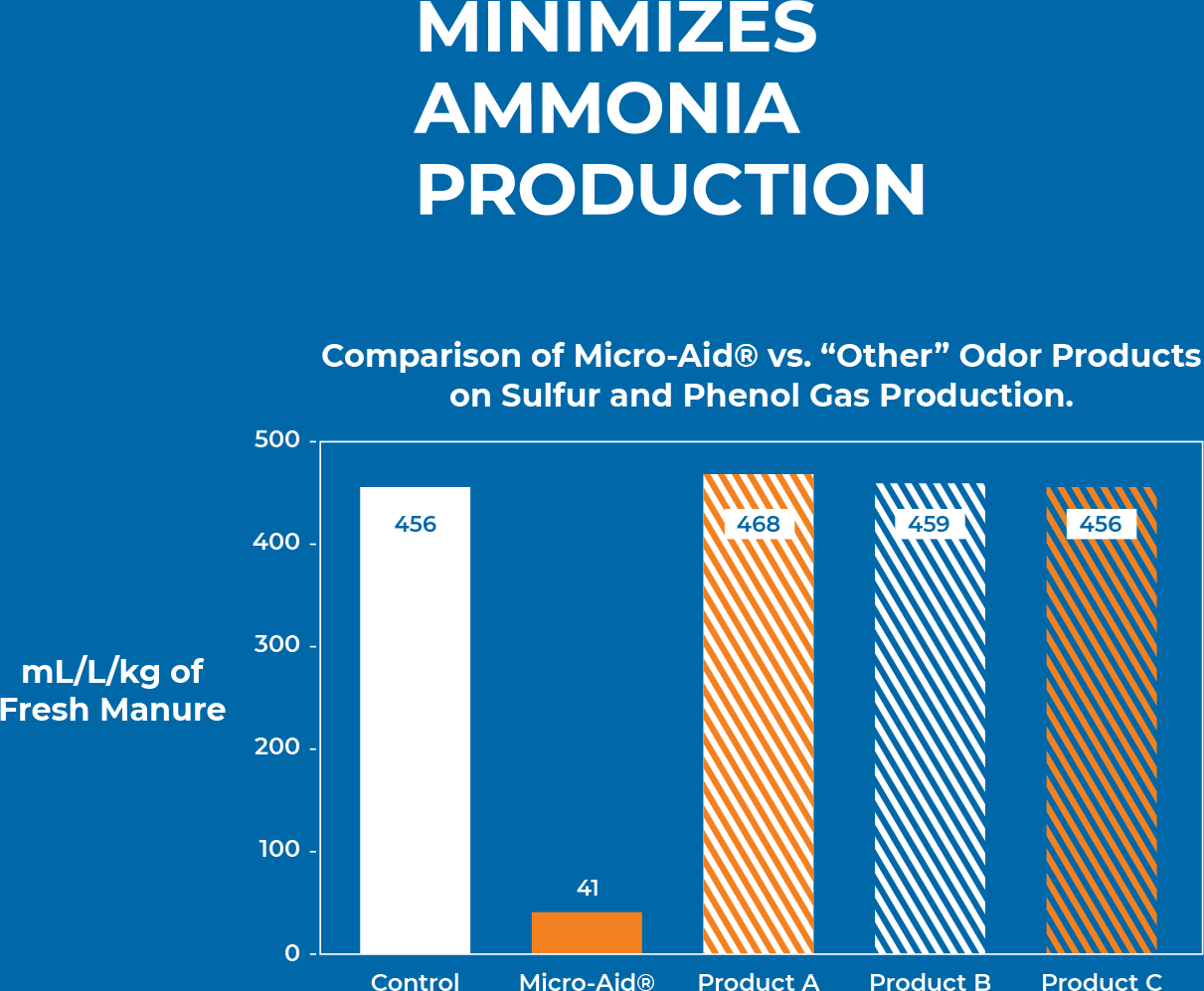
Reduces the production of ammonia and other noxious gases, resulting in healthier animals, reduced odor, and better neighbor relations.
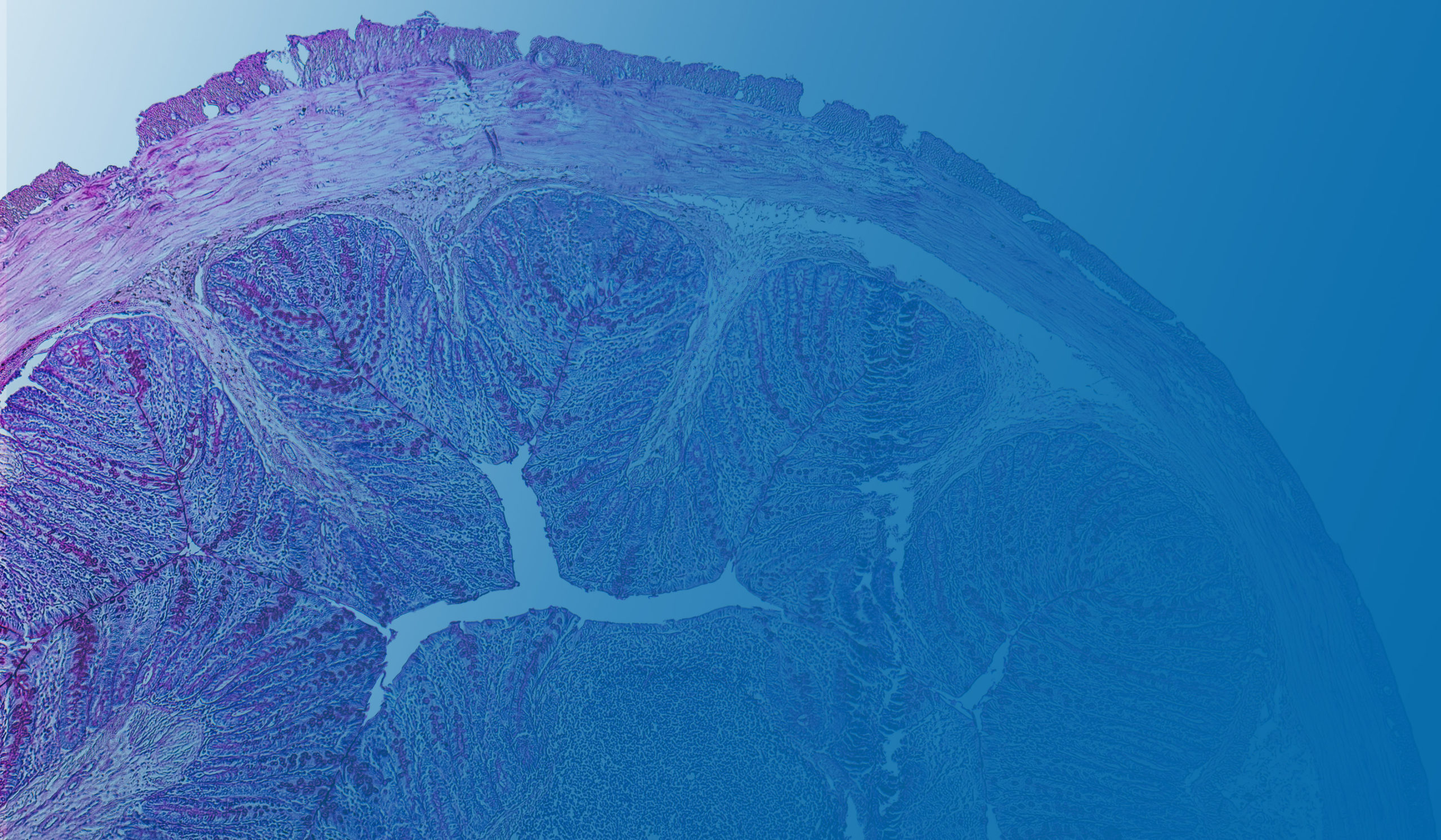
Micro-Aid® Promotes a Healthier Gut Environment

Furthers Tolerable Anti-Microbial Usage
Micro-Aid® is not absorbed by the intestinal tract, instead, it passes through the animal and is excreted along with fecal matter into the waste management system.

Micro-Aid® and Nitrogen Cycle Relationship
Micro-Aid® works both enterically to promote the digestion of nutrients, as well as within the manure to utilize undigested nutrients in forming organic nitrogen compounds while preventing the formation of noxious gases such as ammonia. This reduction in volatilization of ammonia that occurs positively impacts the total nitrogen concentration of manure.
Impacts on Livestock
Micro-Aid® is as effective in today’s commercial livestock industry as it was when it was first introduced over fifty years ago. Performance and health benefits have been reported in growing swine, feedlot beef cattle, broilers, lactating dairy cows, dairy rebreeding performance, sow and litter performance, layers, turkeys, rabbits, horses, pets, and aquaculture.
The following bullet points summarize some of the well-documented performance improvements from extensive research with Micro-Aid® :
Swine
The average improvement in feed efficiency across 17 university, feed industry, and commercial experiments was 3.35%, while the average improvement in daily gain through the use of Micro-Aid® in the feed was 4.3%. Furthermore, ten independent research studies conducted at universities, private research farms, and commercial facilities demonstrated an average reduction in stillbirths of nearly 40% and a reduction in pre-weaning mortality of over 21% when feeding Micro-Aid® .
Beef Feedlot
The average improvement in feed efficiency across 18 university, feed industry, and commercial experiments was 4.60%, while the average improvement in daily gain through the use of Micro-Aid® in the feed was 5.3%.
Grazing Cattle
The average improvement in daily gain across six university or feed industry studies was 10.6%.
Dairy
Across 10 university, feed industry, and commercial experiments the average daily improvement in milk yield through the use of Micro-Aid® in the dairy rations was 3.5 pounds.
Broilers
The average improvement in feed efficiency across 22 university, feed industry, and commercial experiments was 2.01%, while the average improvement in daily gain with the use of Micro-Aid® in the feed was 2.32%.
Turkeys
Research experiments consistently demonstrated that Micro-Aid® is effective in improving turkey grow-out performance, including increased final market weight (3.05%) and improved feed efficiency (5.76%).

